【磁共振实验室:卢星宇博士撰文】【仪器设备:600 MHz / 500 MHz核磁共振波谱仪】【地点:4号楼102室磁共振实验室】
去年11月,我们欣赏了Stang教授(JACS主编)的精彩演讲。在其一部分工作中,他重点讲述了应用核磁共振DOSY来估计分子大小。


Figure 1. Moments from Professor Stang's talk at Westlake U.
自扩散常数在测量中以m2 s-1为单位,对于较小分子和较低粘性溶剂,自扩散常数通常较小;反之对于大分子和粘性介质该常数则较大(Figure 2)。例如,在25℃时,水的自扩散常数为2.299E-9 m2 s-1;对于粘度较小的丙酮,其值为4.57E-9 m2 s-1;对于粘度较大的辛烷-1-ol,其值为1.4E-10 m2 s-1。我们实验室的设备能够在1.0E-7至1.0E-14 m2 s-1范围内测量自扩散常数。
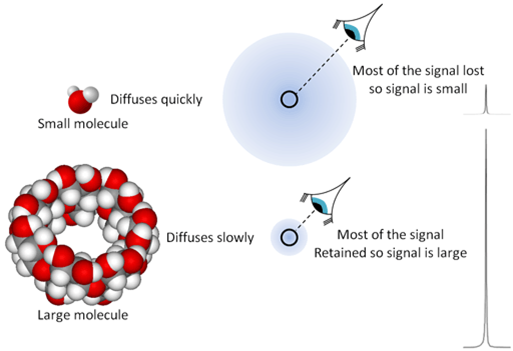
Figure 2. The effect of diffusion rate on signal strength is like focusing on the molecules that have not diffused out of range. Small molecules diffuse quickly leaving few nuclei that refocus while large molecules diffuse slowly leaving more nuclei in place yielding a stronger signal.
分子大小可由Stokes-Einstein方程(Figure 3)估算,其中a是分子的范德华半径(单位:米),k是玻尔兹曼常数(1.38E-23 J K-1),T是开尔文温度,η是溶液的粘度(单位:帕斯卡秒),D是自扩散常数。例如,9,10-二苯蒽在25 ℃下在THF-d8中的自扩散常数为1.04E-9 m2 s-1,粘度为0.501毫帕斯卡秒,应用Stokes-Einstein程计算半径为0.42 nm,与实测的平均范德华半径0.41 nm比较一致。
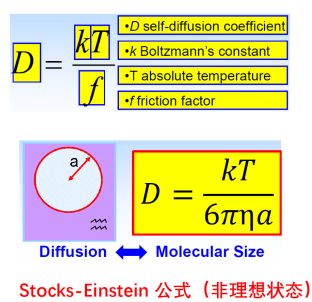
Figure 3. Stokes-Einstein equation.
然而,Stokes-Einstein方程的前提假设是球形分子比溶剂分子大得多。小分子的扩散比预期的快,而大平面分子的扩散比预期的慢。在上述情况下,分子相对于THF-d8的小尺寸被其平面性抵消,从而得到近乎完美的结果(Figure 4)。在离子溶液中,有效扩散半径随着溶剂壳层的增大而增大,明显大于范德华半径。
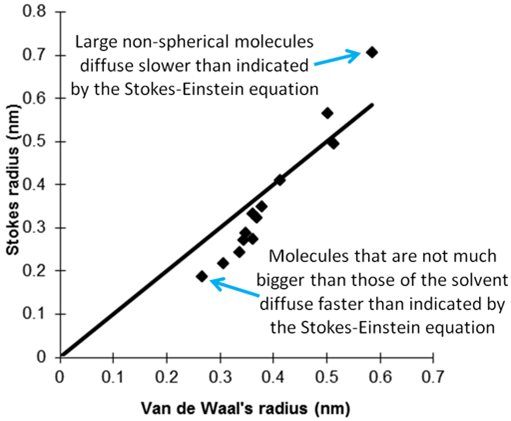
R. E. Hoffman, et al., J. Chem. Soc. Perkin 2, 1998, 1659-1664.
Figure 4. Comparison of the molecular size calculated from the Stokes-Einstein equation with the van der Waals radius.
Stokes-Einstein方程可以更有效地应用于更大的实体,如通常是球形的胶束(Figure 5)。但是,如果液滴内外的磁化率存在显著差异,谱仪的磁场会使胶束发生畸变,扩散速率会随着磁场梯度方向的变化而变化。
J.P.N. Duynhoven, et al., Magn. Reson. Chem., 2002, 40, S51-S59.
Figure 5. Comparison of the emulsion droplet size calculated from the Stokes-Einstein equation with that determined by other methods.
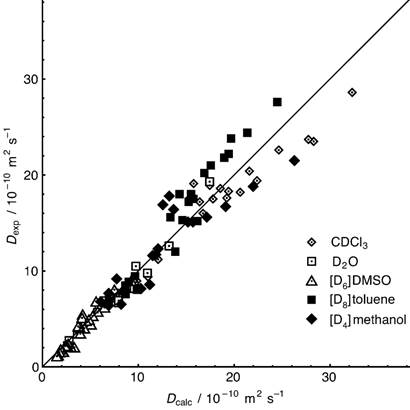
对于分子尺寸的严谨估计还依赖于自扩散常数的准确测量。而为了准确的测量多种不同溶剂中多种不同样品的自扩散常数,往往需要结合理论和经验的方法进行校正。一个适应性较广的加强版Stokes-Einstein关系如Equation 1。Figure 6展示了一个实验数据与该理论预测的相关性的例子,包括溶解于5种氘代溶剂的44种小分子。
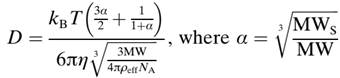
Equation 1.
R. Evans, et al., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3199 –3202.
Figure 6. Measured diffusion coefficient plotted against diffusion coefficient calculated using Equation 1 for 109 samples of 44 small molecules in five deuterated solvents.
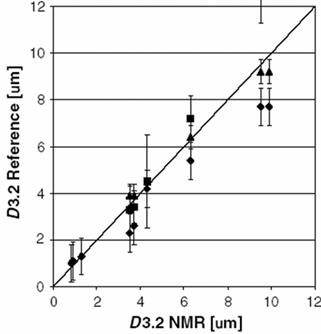
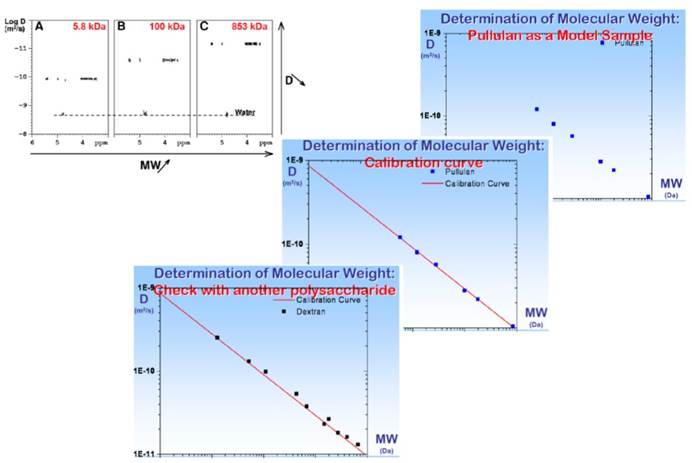
对于大分子分子量的测量,常见的分析技术有动态光散射法、凝胶渗透色谱法等,其不足之处为样品制备比较麻烦。DOSY方法测量分子量具有更广泛的样品适应性,但由于受分子的形状、柔韧性和溶剂化影响,因此需要进行校正。该类校正通常通过在同等溶液环境下对一系列已知分子量的同类样品进行自扩散常数的测量,以建立标准曲线,进而对待测样品进行比对估测(Figure 7)。
S. Viel, et al., Biomacromolecules. 2003, 4, 1843–1847.
Figure 7. 2D DOSY for molecular weight determination in D2O at 300 K of three pullulan fractions of uncharged polysaccharides with different molecular weights.